Skill No 1. Encryption
Introduction
Database encryption increases the security of your data at rest and during transportation. With recent security vulnerabilities, many organisations have taken data encryption seriously. However, database management systems are a common target for attackers because they hold the most valuable asset for most organisations. Once an attacker has gained access to valuable data on your server, they will likely steal it. They then use the data to demand payment in exchange, manipulate data, or achieve monetary profit from the organisation they have attacked.

Security Regulations Compliance
Encryption is one of the most critical requirements for security regulations such as PCI-DSS. It is a statutory requirement. For example, all cardholder data must be encrypted (e.g., AES-256, RSA 2048), truncated, tokenised, or hashed (approved hash algorithms specified in FIPS 180-4: SHA-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384 SHA-512, SHA-512/224, and SHA-512/256). Although this is not the only requisite for having encrypted data, PCI-DSS also needs that the PCI-DSS encryption key management process is supported (we are going to discuss this in the future)
Protecting Sensitive Data
With centralised key management and simple APIs for data encryption, encryption key management is ideal for protecting sensitive data. Examples of these key management include using Hashicorp Vault (open source) if you use the public cloud like OCI Oracle using Oracle’s manage keys, Amazon Web Service (AWS) Key Management, likely also talking about in the near future about this.
Data Encryption…What is it?
Encoding data is the process of encrypting it. It is primarily a two-way function, meaning encrypted data must be decrypted using a valid encryption key. Encryption is one such Cryptography technique. Encryption is a method of concealing information by altering it so that it appears to be random data – encryption methods can make your data (for example, messages) confidential. Still, other techniques and strategies are required to ensure the message’s integrity and authenticity. Encryption is primarily a mathematical process.
There are two basic types for encrypting data in a database. Data at rest and data in transit.
Advantages of Data Encryption
- It ensures the security of all of your data at all times.
- Whatsoever times, privacy and sensitive information are protected.
- It safeguards your data across devices.
- Ensure government regulatory compliance.
- It offers you a competitive advantage.
- The presence of underlying encryption technology for data protection may increase trust.
- Encrypted data is much more secure.
Disadvantages
Encryption employs complex and sophisticated mathematical operations to conceal the meaning of data. Depending on which cyphers or algorithms you use for hashing or deciphering the data. If your database is designed to handle many requests, it will saturate your resources, particularly the CPU.
Attempting to set up data encryption, such as TLS for in-transit or using RSA 2048 bits, can be prohibitively expensive if your financial resources have not been budgeted for this type of consequence. It consumes many resources and puts additional strain on the system’s processor.
Losing the data encryption keys, you will never lose your keys; keep them in a secure place.
Data encryption impacts recovery time, RTO
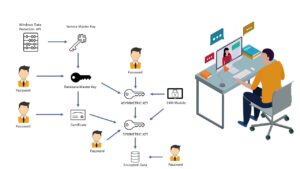
Encryption Architecture
- Extensible Key Management
- Service Master Key
- Database Master Key
- Asymmetric Key
- Symmetric Key
- Certificate
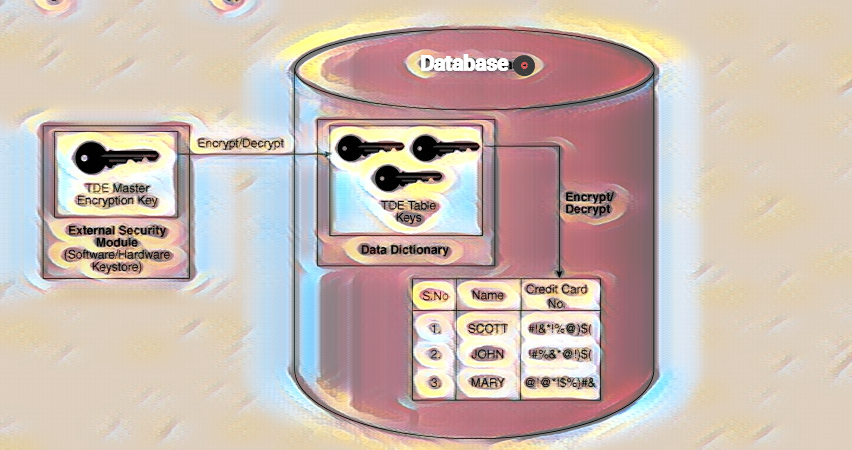
Implement column-level encryption
- Encrypted data cannot be compressed, but compressed data can be encrypted. When using compression, you should compress data before encrypting it for optimal results.
- Stronger encryption algorithms consume more processors and resources. SQL Server 2016, the database can take advantage of hardware acceleration, using Intel AES-NI when performing encryption/decryption tasks.
- Many database engines support algorithms compatibility 130 or above are AES.128, AES-192, and AES-256